Motorcycle standards
The motorcycle standards are set to ensure your bike is safe to ride. These standards cover the design, construction and legal modifications. This is a guide to keeping your motorcycle in a safe and legal condition.
Reference to motorcycles on this page may include mopeds and motor trikes.
The standards for motorcycles, mopeds and motor trikes can vary depending on the Australian Design Rule (ADR) category and the date of manufacture of your bike. (The date of manufacture is usually located on the identification plate affixed to the motorcycle.)
If you do not know the standards and ADRs that apply for your motorcycle, you should consider seeking professional help to design the modifications. You can engage the services of an Approved Person Engineer to provide professional advice. Find an approved person in your area.
There are some general rules that apply to motorcycles modifications:
- Modified motorcycles must continue to comply with the ADRs to which they were originally constructed.
- Modified pre-ADR vehicles must continue to comply with the Transport Operations (Road Use Management—Vehicle Standards and Safety) Regulation 2021
- The alterations must not affect the safe handling of the motor cycle or endanger either the rider or any other road user.
On this page:
Frame and suspension alterations
Modifications to a motorcycle frame or suspension may load vital components well beyond the limits for which they were originally designed. This may increase the probability of failure and may be a danger to the rider and other road users.
Motorcycles with properly designed custom frames, extended forks, hard tail or mono-shock conversions and structural modifications require an engineer’s report to be submitted for approval by the Department of Transport and Main Roads. You must engage the services of an Approved Person Engineer with the LO1 code before starting the modifications. Find an approved person in your area.
Engine replacements and modifications
A replacement engine is acceptable if it is a manufacturer’s option for that model, and the replacement engine does not reduce the effectiveness of the brakes and suspension.
The fitting of any other alternative replacement engine, superchargers or turbochargers will require an engineer’s report to be submitted for approval by the Department of Transport and Main Roads. Engaging the services of an Approved Person Engineer with the LO1 code before starting the modifications is strongly recommended. Find an approved person in your area.
Steering gear
Extended forks may load vital components well beyond the limits for which they were originally designed, making the motorcycle unsafe to ride.
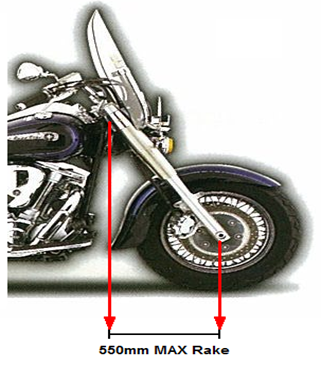
- For motorcycles which have the head stem as the steering pivot point, the horizontal distance from the midpoint between the head stem bearings to the centre of the front wheel must not be over 550mm.
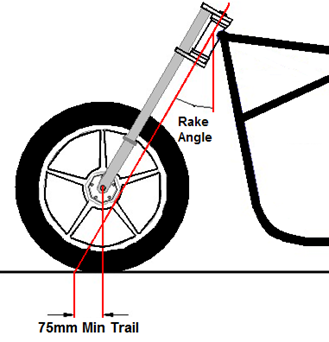
- Offset triple clamps are often fitted to provide the motorcycle with ‘a raked out’ appearance without the need to modify the frame. These are acceptable, provided the trail measurement is not less than 75mm.
Handlebars
ADR 57/00 was introduced for motorcycles manufactured from 1 July 1988. Motorcycles manufactured before this date can apply the ADR 57/00 standards if all sections of ADR 57/00 are met.
Pre-ADR 57/00 compliant
- For motorcycles not complying with ADR57/00, the distance between the extreme ends of the handlebar must not be less than 500mm and not more than 900mm. This measurement does not include mirrors and lights.
- The lowest part of the hand grip on the handlebars must not be higher than 380mm above the attachment point of the handlebars to the motorcycles. When measuring handlebar height, the upper surface of the original steering yoke, not including any spacers, is considered the handlebar attachment point.
ADR 57/00 compliant
- For motorcycles that are compliant with ADR 57/00, the distance between the extreme ends of the handlebar must not be less than 500mm and not more than 1100mm.
- The height of the lowest part of the handgrip above the lowest part of the upper surface of the driver’s seat must not exceed 380mm.
- ADR 57/00 requires all mandatory switchgear fitted to the handlebars to be operable without removal of the hand from the handgrip throughout its full range of movement.
Mandatory switchgear for ADR57/00
| Left hand side | Right hand side |
|---|---|
| Hand lever controlling the clutch | Hand lever controlling front wheel brake |
| Direction indicator control (if fitted to left handlebar) | Direction indicator control (if fitted to right handlebar) |
| Horn button | Supplemental Engine Stop |
| Headlamp main/dipped beam control |
Rear vision mirrors
- Motorcycles built before 1975 must have at least 1 mirror on the right-hand side. Motorcycles built from 1975 onwards must have at least 1 mirror on each side.
- Mirrors must be fitted so that the rider can clearly see by reflection the road behind the vehicle and any following or overtaking vehicle.
- Mirrors can be flat or convex. Convex mirrors must have identical curvature on both mirrors, with a minimum radius of curvature of 1200mm.
- Additional mirrors, such as wide angle or blind spot mirrors, are allowed, and may have a smaller radius of curvature.
- Motorcycles built from 1991 onwards also have a minimum size requirement of 80cm2 for flat mirrors, and 64.5cm2 for convex mirrors.
Exhaust pipes
- Motorcycles are subject Schedule 1, part 9 of the Transport Operations (Road Use Management—Vehicle Standards and Safety) Regulation 2021.
- Motorcycles manufactured from 1 July 1988 have all components of the Silencing System marked with the name or trade name of the manufacturer. Any replacement part of the system must show the trademark or the name of the manufacturer of the system.
- Motorcycles with a date of manufacture from 1 January 2006 must comply with ADR 83/00, and have a stationary ‘signature’ noise limit.
- Noise testing is conducted according to the National Transport Commission stationary noise test procedure for in-service motor vehicles.
- Exhaust systems should not be replaced or modified if this is likely to increase the vehicle’s noise output beyond that of the unmodified system when in good condition.
Seats
A motorcycle may be converted from dual seat to single seat to reduce the Compulsory Third Party (CTP) insurance premiums. It must be converted back to dual seat if a pillion (passenger) is to be carried. You must update the CTP category and registration details to match the current state of the motorcycle. If you don't, you and the pillion may not be covered in the event of a crash and you may be penalised.
Not all motorcycles are easily convertible to a single seat.
The following requirements must be met when converting motorcycle seats, regardless of impacts to the original design or resale value:
A conversion to single seat must not be easily reversible, and must:
- reduce the seat length to 500mm or less. A removable seat cowl or cover is not an acceptable method of seat reduction.
- remove the pillion foot pegs and disable the mounting points by removing mounting brackets and drilling out threaded holes.
A conversion from single seat to dual seat must:
- provide sufficient seating for the rider and pillion.
- provide footrests for both the rider and pillion.
Wheels and tyres
- On all wheels (including any side-car wheel), the tyre size must be suitable for the rim. Each tyre and rim must be strong enough to support the machine when it is fully loaded.
- A tyre fitted to a motorcycle must be free of any apparent defect that could make the vehicle unsafe.
- A tyre fitted to a motor vehicle must, when first manufactured, have been rated by the tyre manufacturer as suitable for road use at the vehicle’s top speed.
- Most tyre specialists can tell you the right tyre and rim for your motorcycle and the appropriate tyre speed rating.
- All tyres must have a clearly visible tread pattern and a minimum tread depth of 1.5mm across the entire primary tread pattern. Secondary tread may be less than 1.5mm, as shown by the fine lines in the tread pattern below.

Headlights
- All motorcycles must have at least 1 headlight and can have up to 4 additional headlights.
- A motorcycle can also have a headlight modulation system, which is designed to vary the brightness of the headlight at a rate of 200 to 280 flashes a minute when used in daylight conditions.
- A headlight fitted to motorcycles manufactured after 1 October 1991 must be ADR 19 compliant.
- Retro-fitting High Intensity Gas-Discharge (HID) or Light Emitting Diode (LED) headlight bulbs to vehicles not originally offered with the technology generally do not comply with the ADRs because the design of the headlamp reflector is incompatible with the bulb (the light is not focused correctly).
- Entire headlight assemblies (bulb, lens, and housing) can be updated to HID or LED provided the new headlight assembly complies with relevant ADRs.
Indicators
Indicators are required on all motorcycles manufactured after 30 June 1975.
Indicators on motorcycles manufactured after 30 June 1975 and before 1 October 1991 are not required to be ADR 19 compliant.
Indicators on motorcycles manufactured from 1 October 1991 onwards must be ADR 19 compliant. Older motorcycles may be made ADR 19 compliant by meeting all ADR 19 requirements. Partial adoption of ADR requirements on older motorcycles to select only the desired modifications is not permitted. If modifications are made to adopt some ADR requirements, all of those ADR requirements must be met.
Pre-ADR 19 compliant
Motorcycle indicators must:
- be at least 300mm apart
- be at least 350mm above ground level
- when operating, display regular flashes of light at a rate of 45 to 120 flashes per minute
- be wired to an audible or visible device that tells the rider when it is operating
- flash at the same time and rate as any other direction indicator lights fitted on the same side of the vehicle
- if the light faces forwards— be coloured white or yellow
- if the light faces backwards— be coloured yellow, or yellow or red if pre-1973.
ADR 19/00 compliant
Motorcycle indicators must:
- For front indicators – be at least 300mm apart and at least 100mm from the headlight
- For rear indicators- be at least 240mm apart
- be 350mm to 1200mm above ground level
- be coloured amber
- light flashing frequency of 60 to 120 flashes per minute
- have compliance markings (e-mark).
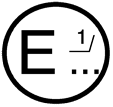
Example of e-mark
- have either a green operating tell-tale light, or auditory tell-tale, or both.
ADR 19/02 compliant
Motorcycle indicator requirements listed above for ADR 19/00, with the following exception:
- Front indicators may be 240mm apart, with the minimum distance from the headlight dependent on the indicator intensity.
| Minimum indicator density (cd) | Minimum separation (mm) |
|---|---|
| 90 | 75 |
| 175 | 40 |
| 250 | 20 |
| 400 | ≤20 |
- Rear indicators may be 180mm apart.
Chain or belt guard
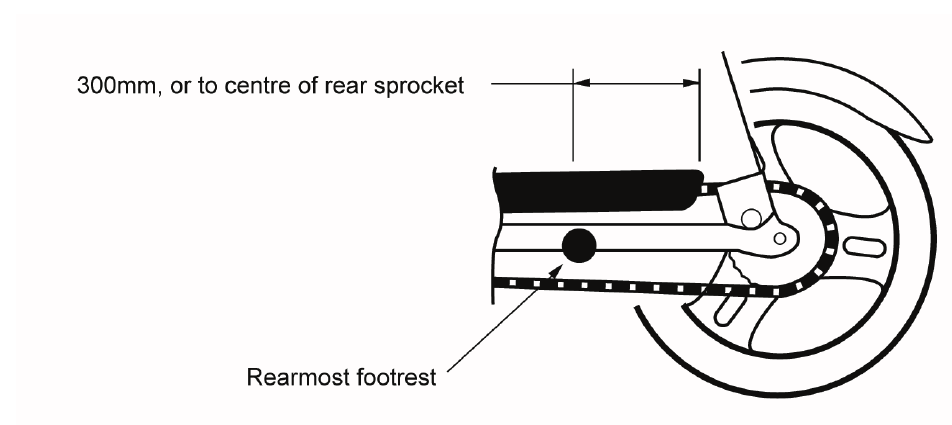
Motorcycles with either chain or belt drive must have a guard to protect the rider and pillion. Protection must be provided for at least the front sprocket/belt drive and upper part of the chain or belt by the frame, other part of the motorcycle or a guard. The chain/belt must be protected to at least 300mm to the rear of the rearmost footrests, or to at least the centre of the rear sprocket.
Mudguard
- A mudguard must be fitted to all wheels (including the sidecar wheel), unless the body or part of the body of the motorcycle acts as a mudguard.
- Each mudguard must be at least as wide as its respective wheel and tyre over the entire length of the mudguard.
- The wheel guards must be designed to protect other road users, as far as practicable, against thrown-up stones, mud, ice, snow and water and to reduce for those users the dangers due to contact with the moving wheels.
- Motorcycles manufactured after 1 July 1988 must be ADR 42 compliant.
ADR42 compliant
Front wheel
The mudguard must extend not less than from a point vertically above the centre of the wheel rearward to a point not higher than the centre of the wheel or to the point where suitable protection is provided by the frame or other construction of the motorcycle when loaded to a mass of 45 kg.
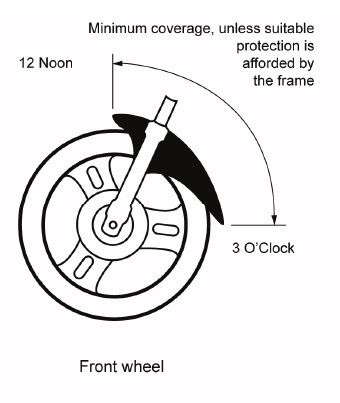
Rear wheel
- The requirement for the rear mudguard to extend to a 45o angle has been removed in the latest ADR. Reducing the length of the rear mudguard to ADR 42/04 requirements is permitted provided it meets all the following requirements:
- it continues to protect other road users, as far as practicable, against thrown-up stones, mud, ice, snow and water and to reduce for those users, the dangers due to contact with the moving wheels.
- all brake, taillights and the number plate light are positioned in compliance to current ADRs.
- the number plate is visible from 20m within an arc extending 45o to each side and above, and horizontally to the rear.
Number plate
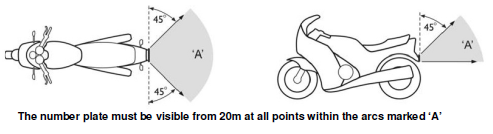
The number plate issued for a vehicle must be permanently attached to the vehicle so that, if the vehicle is on level ground the number plate is:
- in an upright position parallel to the vehicle’s axles
and - not more than 1.3m above ground level
and - the characters on the number plate are visible from 20m away at any point within an arc of 45º from the surface of the number plate above or to either side of the vehicle.
Any cover on the number plate must—
- be clear, clean, untinted and flat over its entire surface
and - have no reflective or other characteristics that would prevent—
- the successful operation of a photographic detection device
or
- the number plate from being legible.
- the successful operation of a photographic detection device
The number plate must be in a clearly legible condition, including being clearly legible from any position from which it is required to be visible.
Brake light
- A brake light must be fitted to the rear of a motorcycle built after 1934.
- When on, a brake light must show a red light visible 30m from the rear of the vehicle.
- Motorcycles manufactured after 1 October 1990 must be ADR 19 compliant.
Pre-ADR 19 compliant
If only 1 brake light is fitted to a vehicle, it must be fitted in the centre or to the right of the centre of the vehicle’s rear.
The centre of a brake light must be—
- at least 350mm above ground level
- not over 1200mm above ground level.
ADR 19 compliant
The centre of a brake light must be—
- at least 250mm above ground level
- not over 1500mm above ground level
- visible from within an arc extending 450 to each side and above
Taillight
- A motorcycle must have at least 1 taillight fitted on or towards the rear of the vehicle.
- If only 1 taillight is fitted to a vehicle, it must be fitted in the centre or to the right of the centre of the vehicle’s rear.
- The taillight must be red and be visible for 200m to the rear of the motorcycle.
- Motorcycles manufactured after 1 October 1990 must be ADR 19 compliant.
ADR 19 compliant
The centre of the taillight must be—
- at least 250mm above ground level
- not over 1500mm above ground level.
The taillight must be at the rear of the motorcycle.
Reflectors
Mandatory
- All motorcycles must have at least 1 rear-facing red reflector which is visible from either side of the rear of the motorcycle.
- Motorcycles manufactured after 1 October 1990 must be ADR 19 compliant.
- ADR19 mandates 1 or 2 side reflectors on each side, and 1 or 2 front reflectors.
- If more than 1 reflector is fitted to any side of the motorcycle, they must be equal height.
- Reflectors of any colour other than red, white or yellow is not permitted.
- If more than 1 reflector is fitted to the front or rear of the motorcycle, they must be equal height and equal distance each side of the centreline.
Optional for pre-ADR19 motorcycles
A pre-ADR19 motorcycle can have:
- 2 rear-facing red reflectors
- side facing reflectors which are yellow, or:
- white near the front
or
- red near the rear
front facing white or yellow reflectors.
- white near the front
If more than 1 reflector is fitted to:
- any side of the motorcycle, they are to be of equal height.
- the front or rear of the motorcycle, they are to be of equal height and equal distance each side of the centreline.
Sidecars
Sidecars which bolt directly to the motorcycle’s frame without the need for any modifications to the motorcycles are acceptable without specific approval.
Sidecars which require the motorcycle to be modified (for example, welding to the frame) must be approved by the Department of Transport and Main Roads. Before modifying your motorcycles so that a sidecar can be attached, you should engage the services of an Approved Person Engineer, who can submit an application on your behalf. Find an approved person in your area.
A sidecarmust only be fitted to the left-hand side of the motorcycle. However, a motorcycle built before 1 July 1988 may have a sidecar on the right-hand side if it was originally constructed that way.
The motorcycle and sidecar combination must not exceed 2 metres in overall width.
A motorcycle manufactured after February 1976 fitted with a sidecar must have a mechanical parking brake.
A sidecar must be fitted with a parking light within 150mm from the side of the sidecar that is furthest from the motorcycle.
- Last updated 21 July 2022

